gauss
This script returns a pseudo-random number with Gaussian or normal distribution, meaning the values returned tend to cluster around a given average or mean value. This could be useful if one needed a random behavior or outcome where deviations from the desired target become more rare as the magnitude of the deviation increases.
An example use might be an enemy AI whose skill is represented by the
degree of error in its aiming ability. If a target is at 90 degrees,
aim = gauss(90,5) would return a firing direction with a small degree
of error. This degree of error (or deviation) is controlled by the second
argument. In this case, the value returned would be within 5 degrees
(one standard deviation) of the desired direction (the mean) about 68% of
the time, and within 10 degrees (two standard deviations) about 95% of the
time. The lower the given deviation, the greater chance the returned value
will be near the given mean, and the more accurate the aim of the AI would be.
From the Wikipedia entry on normal distribution:
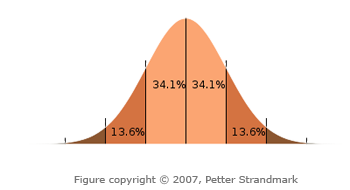
In probability theory, the normal (or Gaussian) distribution is a continuous probability distribution that is often used as a first approximation to describe real-valued random variables that tend to cluster around a single mean value. The graph of the associated probability density function is "bell"-shaped, and is known as the Gaussian function or bell curve:
$$f(x) = \frac{1}{\sqrt{2\pi\sigma^2}} e^{ -\frac{(x-\mu)^2}{2\sigma^2} }$$
where parameter \(\mu\) is the mean (location of the peak) and \(\sigma^2\) is the variance (the measure of the width of the distribution). The distribution with \(\mu = 0\) and \(\sigma^2 = 1\) is called the standard normal.
- gauss(mean,deviation)
- Returns a pseudo-random number with an exact Gaussian distribution.
COPY/// gauss(mean,deviation)
//
// Returns a pseudo-random number with an exact Gaussian distribution.
//
// mean mean value of the distribution, real
// deviation standard deviation of distribution, real
//
/// GMLscripts.com/license
{
var x1, x2, w;
do {
x1 = random(2) - 1;
x2 = random(2) - 1;
w = x1*x1 + x2*x2;
} until (0 < w && w < 1);
w = sqrt(-2 * ln(w)/w);
return argument0 + argument1 * x1 * w;
}
Contributors: Yourself
GitHub: View · Commits · Blame · Raw

